Hydraulic hoses form the lifelines of countless industrial and commercial operations. Hydraulic hoses enable the efficient transfer of pressurized fluids. These hoses are pivotal in diverse sectors such as construction, manufacturing, and transportation. Hydraulic hoses can withstand extreme pressures and environmental conditions. As a result, they ensure seamless fluid transmission due to their precise engineering. The hydraulic hose manufacturing process involves several precise steps. These steps produce flexible, high-pressure hoses in various industrial and commercial applications. Here’s an overview of the typical manufacturing process.
Selection of Materials:
Material selection is the most essential aspect of hose manufacturing. Choosing a suitable material defines your product’s durability and efficiency. Materials like synthetic rubber compounds Nitrile, Neoprene, and Ethylene Propylene Diene Monomer are best. These materials are really good at resisting hydraulic fluids, heat, and wear. They ensure the liquids don’t leak, even when there’s a lot of pressure.

For the inner surface, strong steel wires are best. These wires are tough and light, and they can handle much pressure without getting squished. This process helps the hose stay strong and not burst, even when things get tough.
The outer surface of the hose has synthetic rubber blends. This layer protects the hose from abrasion, ozone, UV radiation, and chemical exposure.
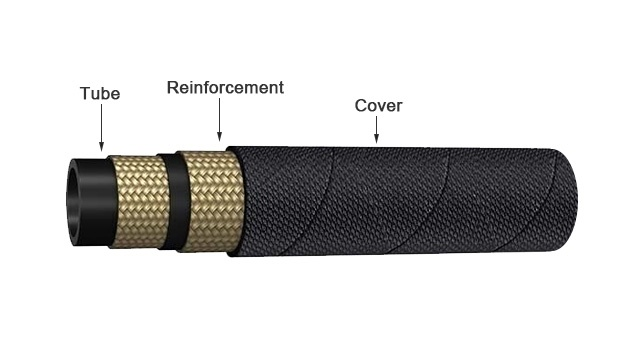
Preparation of Inner Tube:
Creating the inner tube is a crucial step in making hydraulic hoses. The inner tube impacts how flexible and robust the hose will be and how well it can handle hydraulic fluids.
The suitable rubber decision depends on what fluids and conditions the hose will face. Nitrile, Neoprene, EPDM, and Fluoro-elastomers are standard options. They have different strengths, like resisting oil, heat, or chemicals. Once the rubber is chosen, it’s mixed with other things to improve it. These things, like speed-up chemicals and protectors, are added to the rubber to give it the right qualities. This mixture becomes a smooth and even material.
After that, this mixture is put into a machine. The machine then heats it and pushes it through a particular mold to make a shape with the right size and form. Or, it can go through rollers to become the right thickness and uniformity. As all this happens, the temperature and pressure. This process makes sure the rubber gets solid and rigid. The final inner tubes can stand up to hydraulic fluids, bend without breaking, and have smooth insides for fluid to flow easily.
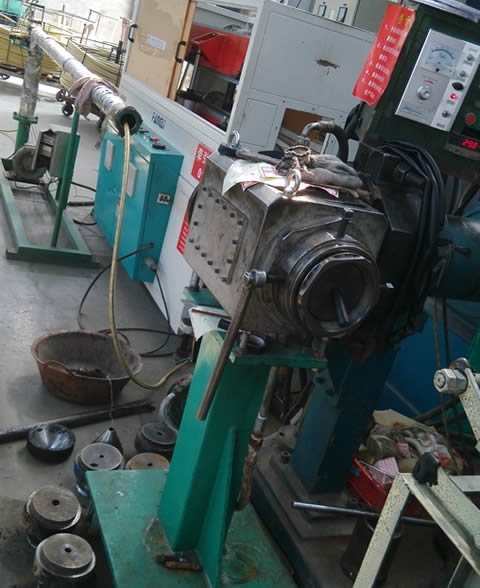

Reinforcement Layer Application:
Adding the reinforcement layer to hydraulic hoses makes them strong enough to handle high-pressure situations. This reinforcement can be done by weaving or spiraling strong steel wires smartly.
In the weaving process, many wires are crossed diagonally over the inner tube at specific angles like 45 degrees, 60 degrees, or 90 degrees. These wires make the hose balanced and flexible. As a result this process, even the spread of pressure, helps the hose to handle bending and pulsing pressures without any problem.

Spiraling, on the other hand, means wrapping steel wires around the inner tube in a spiral pattern. Twisting is suitable for hoses that need to be flexible and handle movements in a straight line. The number of wire layers and how they are wrapped depends on how the hose needs to perform.

In both ways, glue can strengthen the bond between the reinforcement and the inner tube. The chosen method depends on the application of the hose. How much pressure it needs to handle, and how flexible it needs to be.
Cover Application:
After the reinforcement process, the outer cover is added to protect the reinforcement and inner tube from external factors. The cover is extruded or wrapped over the reinforcement layer using a similar process as the inner tube. The Outer cover can be customized. Some additives can be added to improve resistance to specific chemicals, abrasion, or UV degradation. Surface patterns, such as ribs or grooves, can be added to enhance grip and flexibility.

Curing Process Hydraulic Hose Manufacturing:
Curing in the hydraulic hose manufacturing process imparts essential mechanical and chemical properties.
During vulcanization, the polymer chains in the rubber compounds form crosslinks. These crosslinks enhance strength, durability, and resistance to extreme conditions. The curing process achieves the optimal balance between structural integrity and flexibility. The vulcanization process occurs within an autoclave or vulcanization press. where the elevated temperatures range from 140°C to 165°C (284°F to 329°F).

This controlled application of heat and pressure enhances the properties of the hose. It ensures that the rubber compounds transform from plastic to elastic states.
Pressure Test Hydraulic Hose Manufacturing:
Pressure testing guarantees the reliability and safety of the final product.
Burst Pressure Testing verifies the hose’s structural integrity. Burst Pressure Testing checks the hose’s strength by putting more pressure than it should handle. This test makes sure the hose won’t break if pressure goes up. We increase the pressure until the hose bursts and note the highest pressure.
In the Impulse Test, hoses undergo cycles of pressurization and depressurization. The number of cycles a hose withstands before failure indicates its durability and resistance to fatigue. This test helps manufacturers predict the hose’s lifespan under dynamic conditions. This test helps in designing hoses capable of prolonged service.
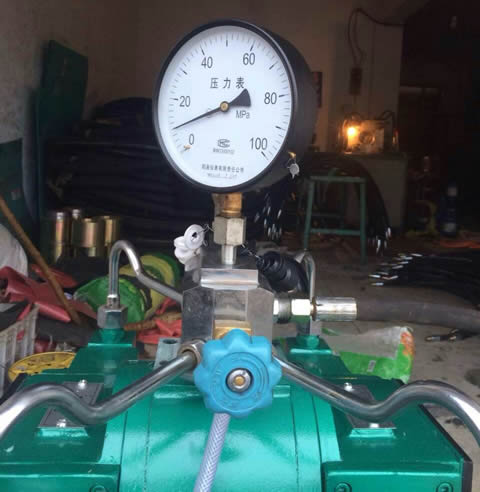

The Leakage Test looks at how well the hose is precise. The pressure is set up, and we use a solution to find leaks. This careful look ensures the connection doesn’t leak, stopping fluid loss or pollution. All these tests prove the hoses are quality-suitable, work well, and are safe. This test tells users that the hoses are ready to use.
Quality Control and Testing:
Quality control and testing are pivotal stages in the hydraulic hose manufacturing process. The QC confirms that each hose conforms to stringent standards of performance and safety. Visual inspections scrutinize every detail, from the hose’s surface finish to the accuracy of its dimensions. This practice guarantees a flawless external appearance. Precise dimensional measurements check if the hose matches the exact designs.

Tests check how well the hose handles challenging situations. These tests put the hose through higher pressures than it should run, like in actual cases, to stop unexpected problems. There’s also a test to see if the hose can take ozone in the environment without breaking down. Another test bends the hose a lot to see if it lasts. And they also check how well the hose works in different temperatures.
Packaging Hydraulic Hose Manufacturing:
After the clearance from the QC department, the next step is packing and finishing. The information, such as pressure ratings, manufacturing dates, and specifications, is available on the tags. Proper packaging ensures the hoses remain protected during transportation and storage.

Summing things up, this article is a complete guide to manufacturing hydraulic hoses. The Hydraulic Hose Manufacturing needs tight tolerance and precision. Expert engineers and fabricators are a must for a perfect design.